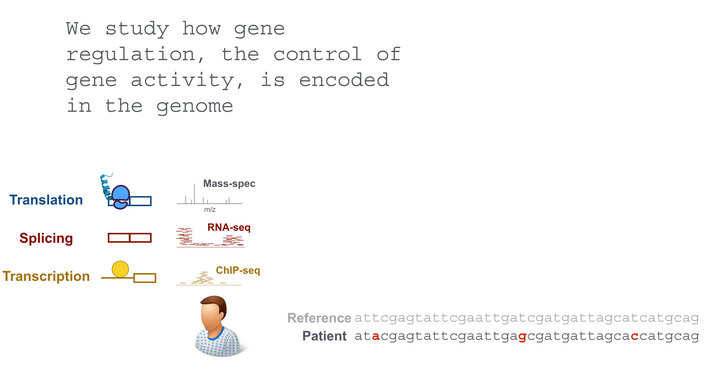
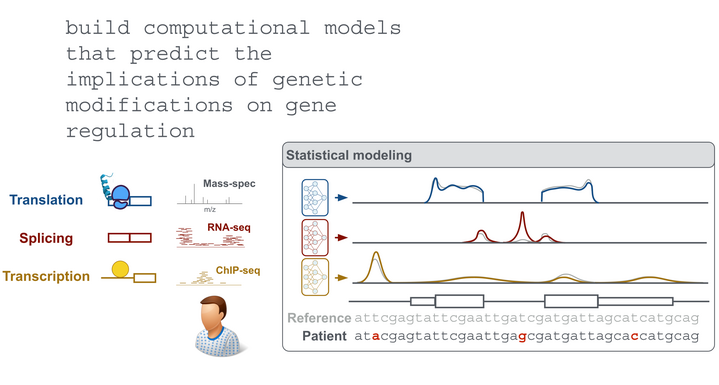
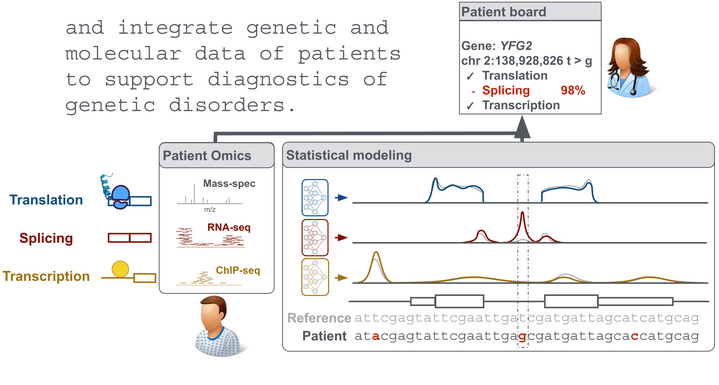
Computational Biology
Our goal is an improved understanding of the genetic basis of gene regulation and its implication in diseases. To this end, we employ statistical modeling of 'omic data and work in close collaboration with experimentalists.
Affiliations
On top of our main affiliation at the School of Computation, Information and Technology, we are proud members of the School of Medicine, the Munich Data Science Institute, and the Computational Health Center of Helmholtz Munich.
Moreover, our lab is part of the graduate schools Munich School for Data Science and Quantitative Bioscience Munich.
Selected Publications
Clarke, Holtkamp, et al. Integration of variant annotations using deep set networks boosts rare variant association testing, Nature Genetics (2024)
Wagner et al. Aberrant splicing prediction across human tissues. Nature Genetics (2023)
Mertes et al. Detection of aberrant splicing events in RNA-Seq data with FRASER. Nature Communications (2021)
Avsec et al. Base-resolution models of transcription factor binding reveal soft motif syntax. Nature Genetics (2021)
Avsec et al. The Kipoi repository accelerates community exchange and reuse of predictive models for genomics, Nature Biotechnology (2019)
Cheng et al. MMSplice: modular modeling improves the predictions of genetic variant effects on splicing, Genome Biology (2019)
Brechtmann et al. OUTRIDER: A statistical method for detecting aberrantly expressed genes in RNA sequencing data, American Journal of Human Genetics (2018)
Kremer et al. Genetic diagnosis of Mendelian disorders via RNA sequencing. Nature Communications (2017)
Schwalb et al. TT-seq maps the human transient transcriptome. Science (2016)
Eser et al. Determinants of RNA metabolism in the S. pombe genome. Molecular Systems Biology (2016)
Bader et al. Negative feedback buffers effects of regulatory variants. Molecular Systems Biology (2015)
Gagneur et al. Genotype-environment interactions reveal causal pathways that mediate genetic effects on phenotype. PLoS Genetics (2013)